- Published on
Debug Regular Expressions Fast with Our Live Regex Tester
- Authors

- Name
- Adam Johnston
- @admjski
Regular expressions are one of the most powerful—and intimidating—features in modern programming. A well‑crafted pattern can extract data, validate input or refactor huge codebases, but many developers avoid regex because the syntax feels opaque. The Regex Tester changes that. It lets you experiment with patterns in real time, highlights matches as you type and reveals capture groups and replacements instantly, all inside your browser with no data leaving your machine.
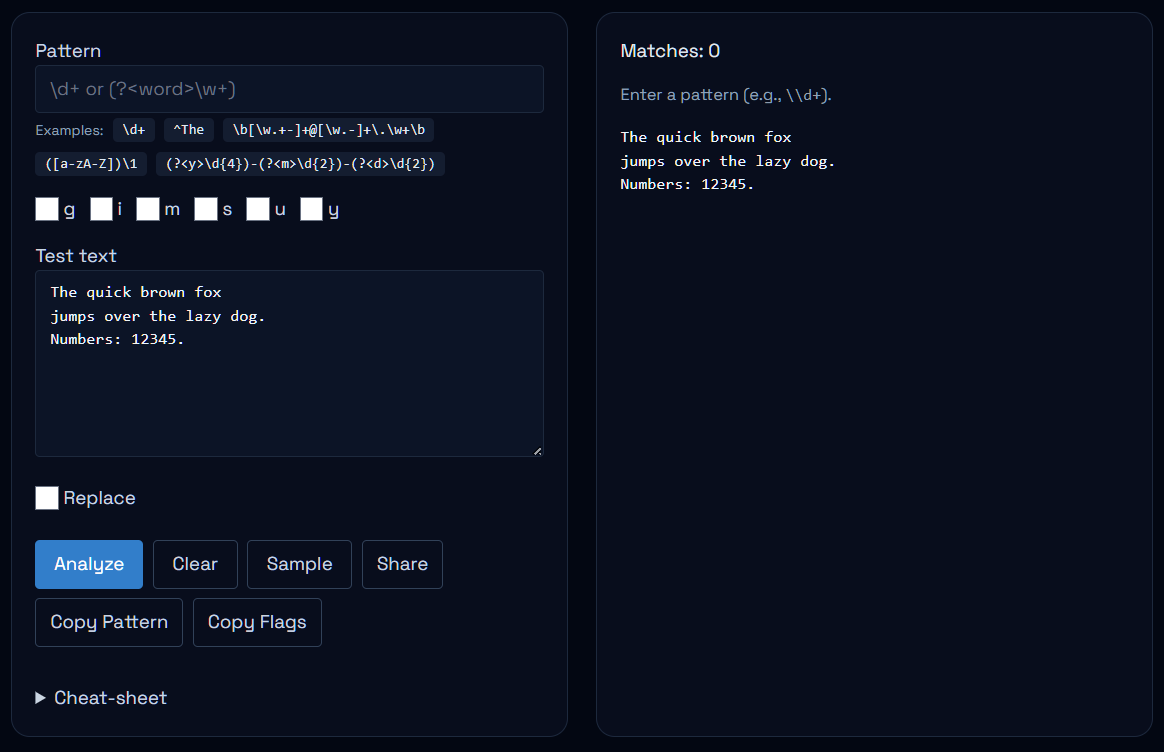
Why a dedicated Regex Tester matters
Every programming language ships with its own regex engine, but figuring out the right pattern usually happens outside the code editor. Copy‑pasting into console windows or writing temporary scripts slows down the feedback loop. Our tester gives you a focused workspace where the pattern, sample text and results sit side by side. Highlights update immediately with each keystroke, so you can watch your pattern evolve without rerunning commands.
- Live highlighting shows exactly which parts of the sample text match.
- Capture group breakdown lists groups and their contents, making nested patterns less mysterious.
- Replace mode lets you preview substitutions before touching your real data.
- Export options copy matches as JSON or CSV for quick reuse.
The tool uses the same JavaScript engine that powers browsers, which means patterns you craft here will behave the same way when embedded into client‑side scripts or Node.js utilities.
Getting started with the Regex Tester
1. Load the tool
Open the Regex Tester in your browser. No signup is required and everything runs locally. You will see three panes: one for the regex pattern, one for flags like global or case insensitive, and a larger area for sample text.
2. Enter a pattern
Begin with a simple expression such as \d+ to match numbers. As you type, any numbers in the sample text glow with a subtle highlight. The match list below the editor shows each instance with its index positions.
3. Refine with groups and alternation
Want to capture phone numbers in multiple formats? Try a pattern like (?:\+\d{1,3}\s?)?(\d{3})[\s-]?(\d{3})[\s-]?(\d{4}). The tester displays each capture group, so you can verify the area code, exchange and line number separately. If parts of the number fail to highlight, tweak the pattern and immediately see whether the change fixes the issue.
4. Test replacements
Switch to Replace mode and enter something like $1-$2-$3. The output shows your sample numbers reformatted with dashes. This preview prevents the dreaded “replace all” mishap that can corrupt thousands of lines in an editor.
5. Copy results
When satisfied, copy the matches as JSON to feed into scripts or as CSV for a spreadsheet. You can also save the pattern and test text to revisit later.
Real‑world use cases
Data validation
Form fields often need quick validation before hitting a backend. With regex you can ensure emails, dates or custom identifiers follow a strict format. For example, a simple email pattern ^[^\s@]+@[^\s@]+\.[^\s@]+$ catches most invalid addresses. Testing it in the tool with a variety of sample inputs helps you understand edge cases like subdomains or plus addressing.
Search and replace in code
Refactoring a codebase sometimes requires sweeping modifications, such as converting callbacks to async functions or renaming a batch of variables. The Replace mode shows how a pattern will transform each match, making it safer to run the same regex inside your editor or using command‑line tools like sed.
Log file analysis
Sysadmins and developers often parse gigabytes of logs to hunt for specific error codes or traffic patterns. Using the tester, you can prototype a regex that extracts the relevant segments—like timestamps or IP addresses—before running it over an entire log file in a script.
Web scraping and data cleanup
When scraping HTML or cleaning messy CSV exports, regex can strip tags, normalize whitespace or isolate numeric values embedded in text. Crafting the pattern in a friendly interface speeds up the iteration cycle and reduces mistakes that would otherwise pollute the dataset.
Tips and best practices
"The more precise your pattern, the less work you do afterward." – a reminder from countless late‑night debugging sessions
- Build incrementally. Start with a small piece, test, then extend. Attempting a complex regex in one shot often leads to frustration.
- Use named groups like
(?<year>\d{4})when the engine supports them. They improve readability and make replacements easier. - Consider performance. Catastrophic backtracking can freeze processes. Resources like MDN’s guide to avoiding exponential blowup explain how to design efficient patterns.
- Document tricky expressions. Comments such as
/(\d{4})-(\d{2})-(\d{2})/u # YYYY-MM-DD/using thexflag (where supported) save future developers from reverse engineering your intent.
Common pitfalls the tester can reveal
Greedy vs. lazy matching
A pattern like "<.*>" swallows an entire HTML block because * is greedy. Adding ? to make it "<.*?>" stops at the first closing bracket. Seeing both behaviors in real time cements the concept faster than reading a definition.
Escaping special characters
Forgetting to escape characters such as . or ? leads to unexpected matches. The tester provides a character helper that reminds you when a symbol has special meaning and inserts the escape automatically if needed.
Unicode surprises
Many regex engines treat characters beyond basic ASCII differently. Our tool supports the Unicode flag u, letting you verify how emojis or accented characters behave before deploying globally.
Suggested visuals
- Annotated screenshot of the tester with callouts for pattern, flags and output panes.
- Diagram showing how a sample string flows through the regex engine, highlighting capture groups.
- Short GIF demonstrating a search‑and‑replace operation.
Learn more about regular expressions
If you are new to regex, the MDN Regular Expressions Guide provides a thorough introduction with interactive examples. For deeper dives, Mastering Regular Expressions by Jeffrey Friedl remains a classic reference.
See how regex interacts with other utilities on InfiniteCurios: try our CSV ↔ JSON ↔ YAML Converter for restructuring data or the Word / Character Counter when preparing clean test strings.
Why trust this guide?
This article was written by Adam Johnston of Infinite Curios, who builds developer utilities used by thousands each month. The Regex Tester itself is open source, so you can review the code or suggest improvements on GitHub.
Conclusion and next steps
Regular expressions unlock powerful text processing capabilities, yet they can feel esoteric without the right tools. Our Regex Tester shortens the learning curve by providing immediate visual feedback, safe replace previews and exportable results. Whether you are validating form inputs, mining logs or cleaning scraped data, practicing inside this sandbox will sharpen your skills and prevent costly mistakes.
Ready to experiment? Open the Regex Tester now and start crafting your next pattern.
Further looks

